Outlines
Dealing with IndexError in Python: Accessing Out-of-Range Elements
Handling errors is an integral part of programming, and in Python language, we say that it is an IndexError while attempting to get entry to elements past the limits of an information structure is a commonplace occurrence. This submission delves into the nuances of handling IndexError in Python, in particular focusing on the eventualities whilst builders try to get admission to out-of-variety elements inside lists, tuples, or different iterable objects.
Understanding the reasons, impact, and powerful techniques to control IndexError instances is crucial for writing strong and mistakes-tolerant Python code. Join us as we discover practical processes to address and mitigate that out-of-range get-entry to mistakes in Python programming.
What is IndexError in Python?
In Python Programming Language, IndexError is a specific form of exception that takes place when you try to get an entry to an index of a chain (like a list or tuple) that doesn’t exist or is out of the collection’s variety. I often face this error when I work on Python Django. This blunder typically arises when attempting to get admission to an index that is better than the most index or decreases than the minimal index available in the sequence.
Example demonstrating IndexError in Python:
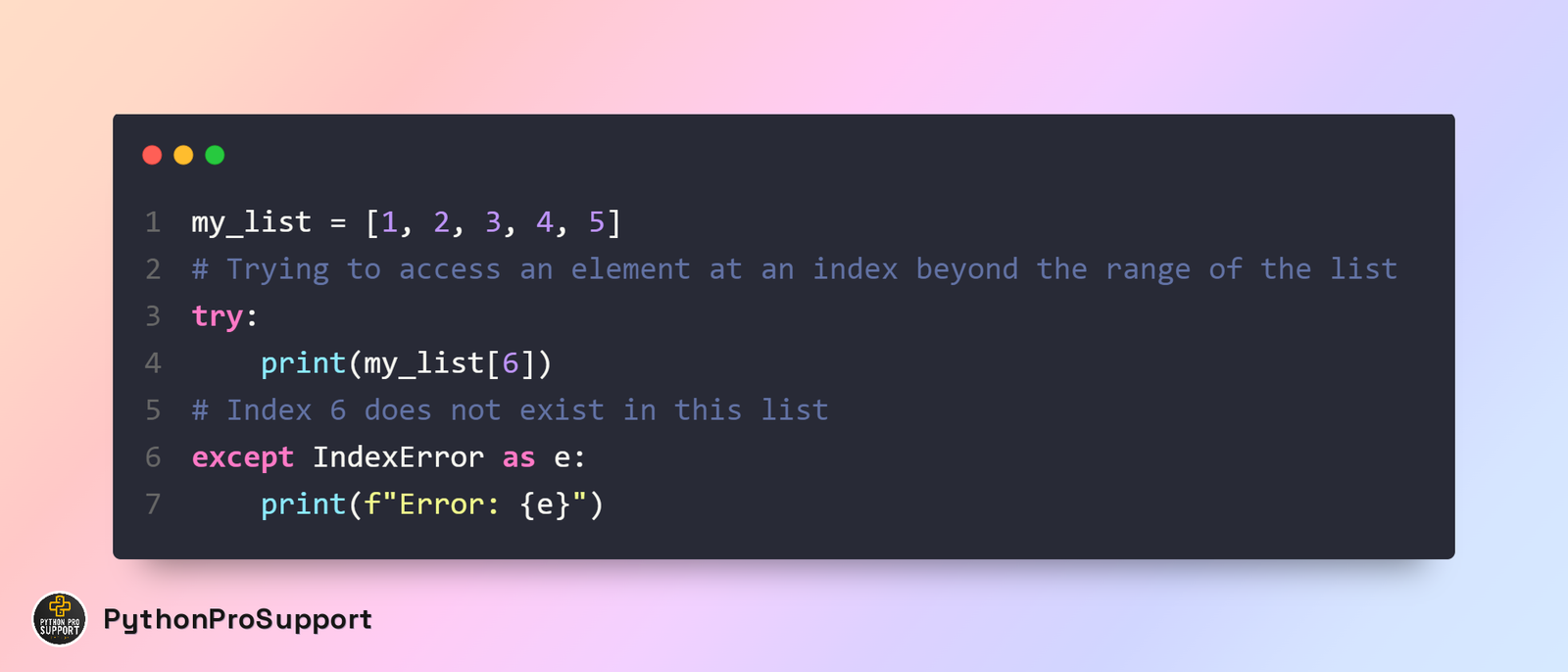
In this example, the listing my_list includes factors from index 0 to index four (general of five elements). However, the code tries to get the right of entry to my_list[6], which is past the range of the listing. As a result, an IndexError is raised at runtime, indicating that the index is out of range.
These mistakes can also arise in different iterable items, consisting of strings, tuples, or arrays while trying to get admission to an index that does not exist inside a certain variety of the collection.
Handling IndexError exceptions using try-besides blocks, as proven in the example, allows you to gracefully manage such conditions via providing custom-designed blunders messages or taking alternative movements to prevent this system from crashing due to an out-of-variety index get right of entry to.
Python IndexError Types with Examples
In Python, IndexError is often encountered while trying to get entry to factors in sequences (which includes lists, tuples, strings, etc.) using indices that are out of the legitimate range for that series. There are some commonplace situations in which IndexError occurs, and here are the sorts with examples:
1. Accessing Elements Beyond the Valid Range
|
1 2 3 4 |
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] # IndexError: Trying to access an index beyond the range of the list print(my_list[5]) # Index 5 does not exist in this list |
2. Accessing Negative Indices Beyond the Valid Range
|
1 2 3 4 |
my_string = "Hello" # IndexError: Trying to access a negative index beyond the range of the string print(my_string[-6]) # Index -6 does not exist in this string |
3. Slicing with Invalid Indices
|
1 2 3 4 |
my_list = [71, 62, 33, 41, 45] # IndexError: Trying to slice with an end index beyond the range of the list print(my_list[2:10]) # End index 10 is beyond the range of the list |
4. Empty Sequences
|
1 2 3 4 |
empty_list = [] # IndexError: Trying to access an element in an empty list print(empty_list[0]) # Cannot access any index in an empty list |
5. Incorrectly Handling Nested Lists
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
# Define a nested list my_nested_list = [ [0, 12, 13], [4, 95, 56], [15, 13, 17] ] # Attempt to access an index that doesn't exist within the nested list try: print(nested_list[3][4]) # IndexError will occur here except IndexError as e: print("IndexError: Trying to access an index within a nested list that does not exist") |
6. Using Invalid Indices in Loops or Iteration
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
my_list = [11, 12, 13, 14, 15] # IndexError: Trying to access indices beyond the range in a loop for n in range(6): print(my_list[n]) # Index 5 is the maximum valid index in this list |
Handling these IndexError situations involves verifying the indices or range of indices being accessed before attempting to access them to prevent the code from raising these exceptions. Using conditional statements or try-except blocks can help manage these scenarios gracefully by providing alternative actions or error messages when index access goes beyond the valid range of the sequence.
Best Practices to Avoid IndexError
To avoid IndexError in Python when working with sequences like lists, strings, tuples, etc., it’s important to follow some best practices:
1. Check Length Before Indexing:
Always verify the length of the sequence before accessing its elements using indices to ensure the index is within the valid range.
Example:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] if len(my_list) > 5: print(my_list[5]) # Safely access index if the length allows else: print("Index is out of range") |
2. Use Try-Except Blocks:
Wrap the code that may cause IndexError in a try-except block to handle the exception gracefully.
Example:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] try: print(my_list[5]) # Attempt to access the index except IndexError: print("Index is out of range") |
3. Use Slicing Instead of Individual Indexing:
Consider using slicing to access a portion of the sequence instead of accessing individual elements by index.
Example:
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] # Safely access elements using slicing sliced_elements = my_list[2:5] # Access elements at indices 2 to 4 print(sliced_elements) |
4. Utilize Conditional Statements:
Employ conditional statements to ensure that the index being accessed is within the valid range before attempting to access it.
Example:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] index_to_access = 5 if 0 <= index_to_access < len(my_list): print(my_list[index_to_access]) # Access if index is within the range else: print("Index is out of range") |
5. Looping with Valid Indices:
When looping through indices, ensure that the indices are within the range of the sequence to avoid IndexError.
Example:
|
1 2 3 4 |
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] for i in range(len(my_list)): print(my_list[i]) # Access elements safely using valid indices |
By following these best practices, you can mitigate the occurrence of IndexError in your Python code and handle situations where index access goes beyond the valid range of sequences, ensuring more robust and error-tolerant programs.
Your Interested Topics:
Debugging ModuleNotFoundError in Python: Resolution Tips
Python Functions: A Step-by-Step Beginner’s Guidelines
Resolving Python AssertionError: Steps for Debugging Assertions
Feel free to proportion this put up across your preferred social networks consisting of Facebook, Twitter, and WhatsApp to spread the information! Don’t overlook joining our YouTube channel for greater insightful content.
